SPM-START
SPM configuration for quick start-up in small and medium-sized plants.
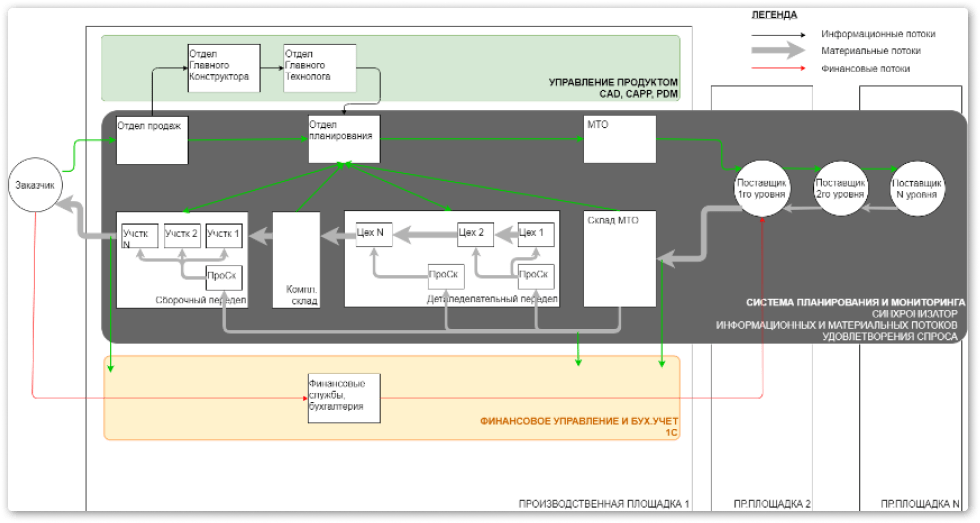
Кросс-классовое ( ERP—SCM— MES— BI) solution based on classical methodologies
MRP II, APS, Lean, TOC, advanced methods SCM, авторских наработок.
Основано на нашей большой и сложной системе СПМ (Lean ERP SCMo) и позволяет вашей системе управления эволюционировать по мере роста предприятия.
It provides specially configured cross-class (ERP-SCM-MES-BI) software based on classic methodologies-MRP-II, Lean, TOC, advanced SCM methods, author's developments, and based on our" large and complex " Lean system for quick start-up for small and medium-sized production businesses ERP SCMo/SPM.
For small manufacturing businesses (dozens of people) and nationalized workshops of large factories
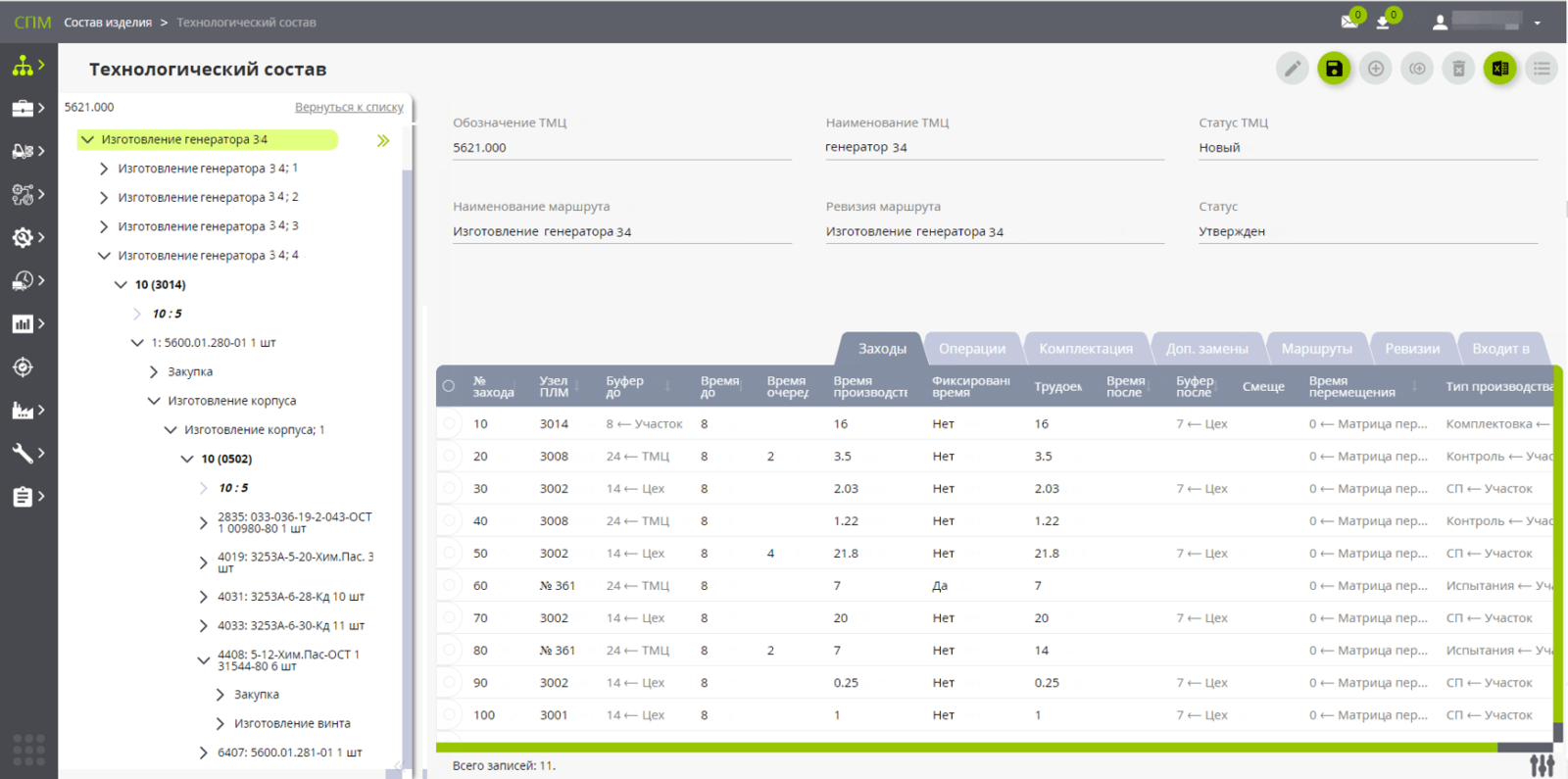
Master Data
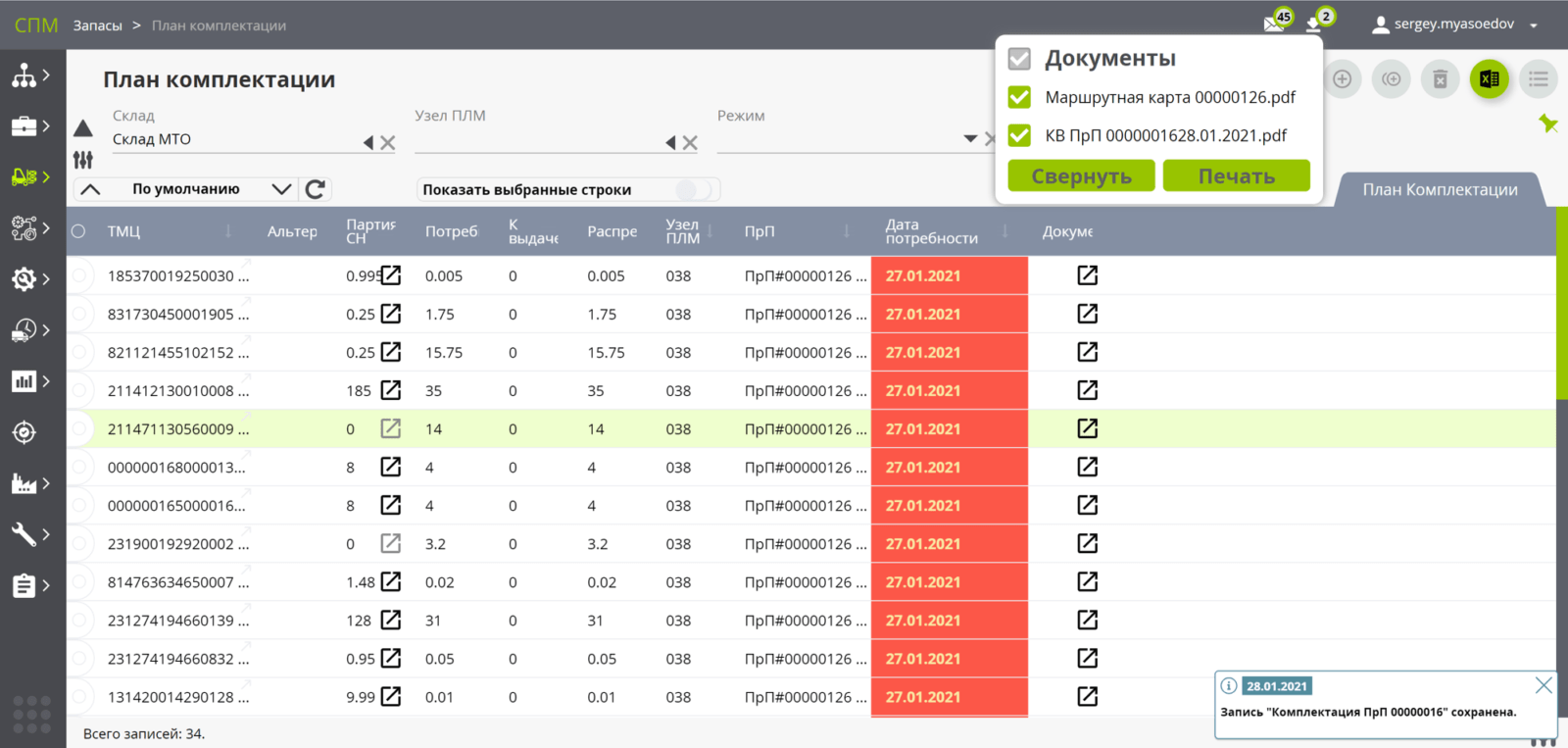
- Production and logistics model: workshops, sites, resource groups and resources, warehouses, including remote ones (with details up to the "row - rack - cell" addresses).
- supplies and materials - materials, PKI, Assembly units, work in progress and finished products.
- Product composition management ("PDM-lite"), which provides work with СИ (КСИ and ТСИ), within the framework of standard PDM functionality, and with synchronization with the planning and production model. With the ability to attach files of drawings, instructions, etc. and their on-line visualization.
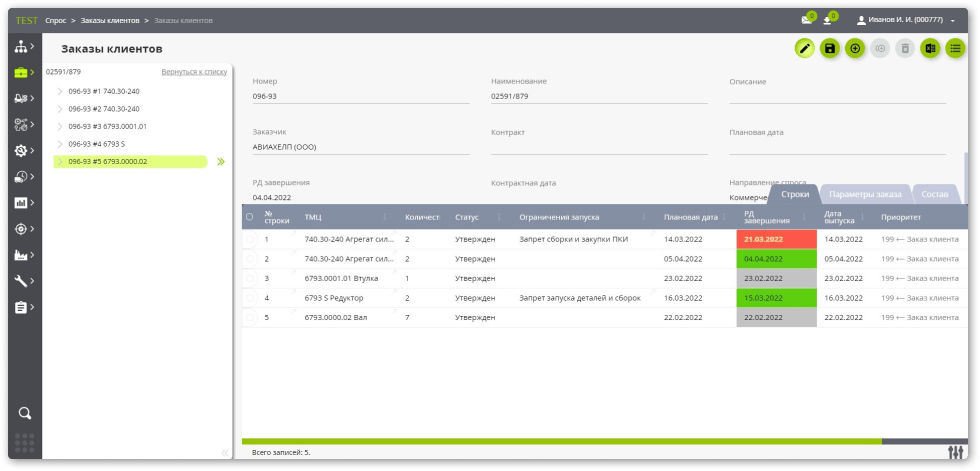
Demand management
- Demand management objects:
- orders from customers with different status;
- forecasts;
- re-order point (non-reduced balance, reserve, insurance/buffer stock);
- the main production plan, including taking into account the analysts of different needs consolidated in the releases of the OPP;
- internal orders (requests),
- production tasks of various types (PrP. CCD),ПрП, ПЗС);
- projects.
- Actions, including schema implementation: "Production-to-order", "Assembly-to-order", "Production-to-warehouse", "Development-to-order":
- determination of the possible product release date at the time of order acceptance (taking into account resources),
- maintaining forecasts of demand for commonly used Assembly units / PKI, with the absorption of forecasts by placed real orders and "parental needs";
- calculation of product production under the release cycle,
- balancing output based on long-term capacity utilization,
- monitoring the status of orders, including those provided to the client,
- configuration and shipment management.
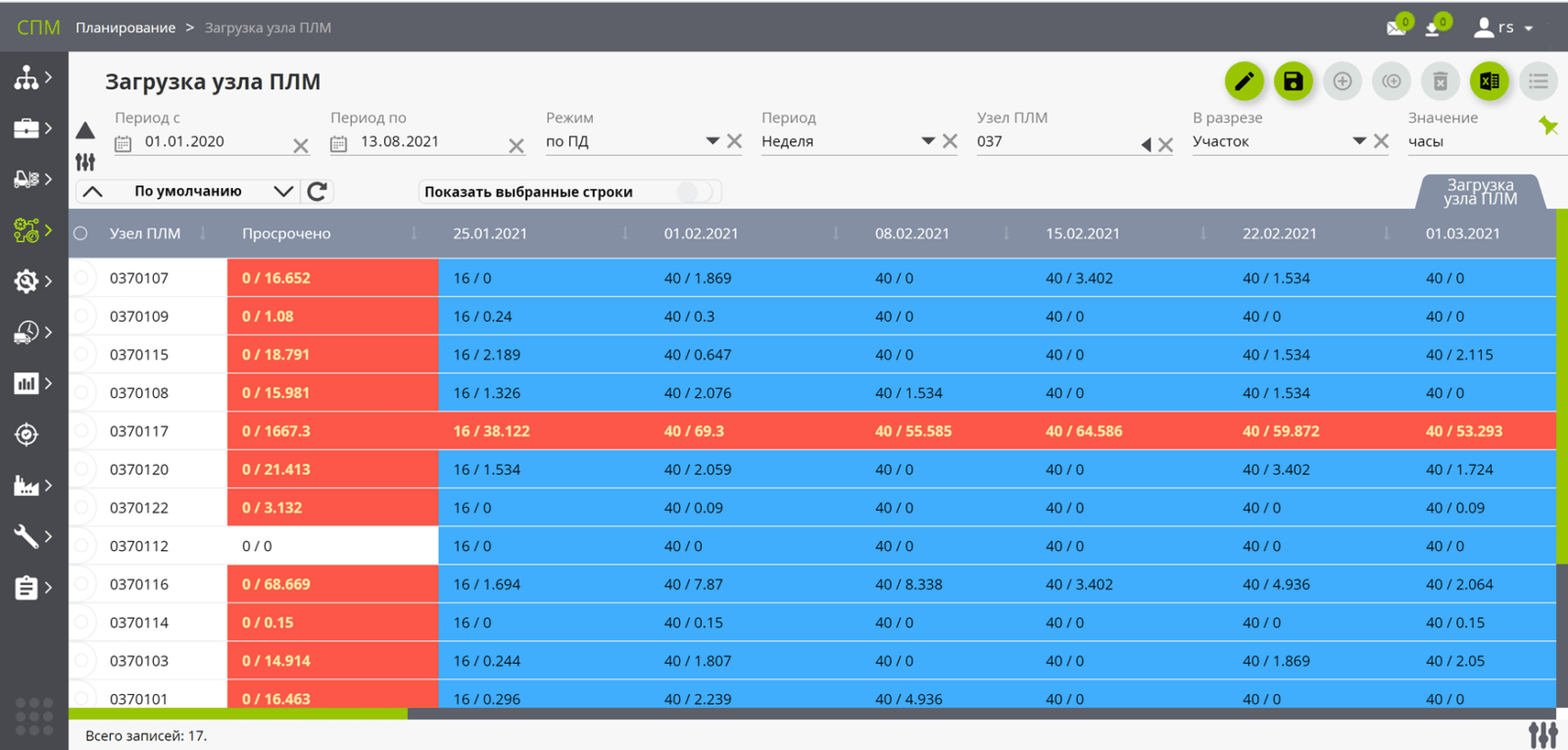
Planning
- Synchronized and pull-out planning of production, supplies (supply chain, cooperation):
- distributed (under demand directions, customers, orders, order lines, instances),
- in expected arrivals for orders to suppliers ("on the way..", etc.),
- release plans for production tasks include;
- taking into account the capacity constraints of production resources in bottlenecks or across all resources;
- taking into account time and quantity buffers;
- with the formation of 2 versions of plans:
- directive plan — "Just in time", on time and in a quantity that meets demand;
- settlement plan-with estimated expected order dates (based on the status "for today");
- based on launch / release priorities.
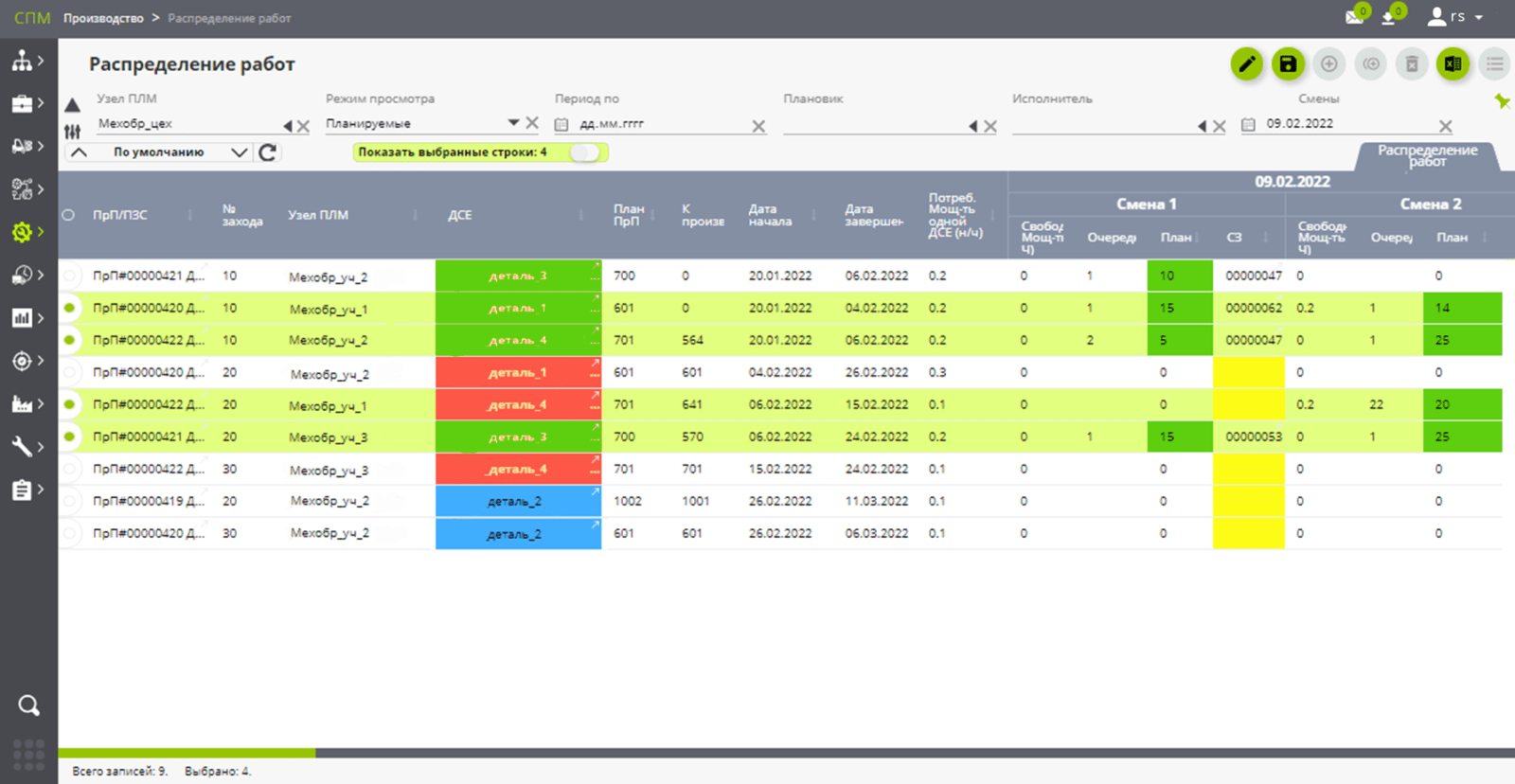
Performance management
- Production (including classic " MES " functionality):
- Start-up management, including pull-up, for external and internal demand, with restrictions on the "start window" and "overflow" (queues or production resources), restrictions for the next few days/shifts (ConWIP*, ConLoad algorithms).
- Formation of production tasks. Different types for different production stages:
- for machining/assembly shops/sites,
- for harvesting operations, short-cycle DSE,
- for complex / long-term (days, weeks) builds.
- Accounting for production progress:
- by precinct, by shift. In general, or up to the level of operations, performers,
- using digital input,
- with "loops" for cooperation/services (without breaking the route), etc.
- With inventory management (ready-made DSE), including buffer warehouses / storerooms (before assembly).
- Deliveries (supply):
launch management (creating orders for suppliers);
tracking orders by stages of the supply chain (preparation of an order / contract – approval/payment — placement with a supplier – production by a cooperative operator – transportation — entrance control, etc.);
acceptance to the warehouse, complete set for the launch plan, transfer to production;
- automatic transfer of information to 1C for accounting.
Monitoring
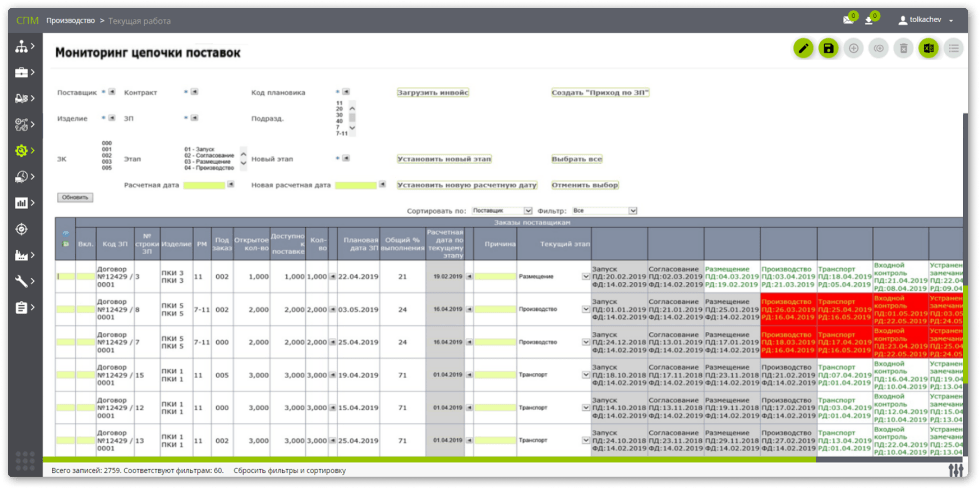
- On-line visualization of what is happening in the context of orders, production, plan / fact (all forms of the system are opened in a web browser):
- "Order readiness" — monitoring of the status of orders (directive/estimated date, deviation, % of readiness for the main stages: procurement — procurement — machining — assembly).
- "Synchronicity" of the work of sites, equipment, and supplies in order to implement "Just-in-time" execution of orders.
- "Order by supply chain" (internal, external by MZK) and "Where is the part".
- Planned, actual, and estimated Gantt chart of order fulfillment.
- Direct production cost:
- planned, by material component, direct labor and direct overhead costs,
- actual, accumulated at the moment, calculated, taking into account the actual.
Integration
- With external systems (1C, PDM, CRM) - через Rest API.